Completely customized according to different customer needs
Contact UsRefractory industry breathable bricks: core materials to resist high-temperature
Permeable bricks are indispensable refractory materials in high-temperature industries (such as iron and steel metallurgy, non-ferrous metal smelting). Their performance is directly related to equipment lifespan, production efficiency, and product quality. This article systematically analyzes the core knowledge of this subfield from aspects such as the definition, production process, performance characteristics, application fields, and industry development trends of permeable bricks.
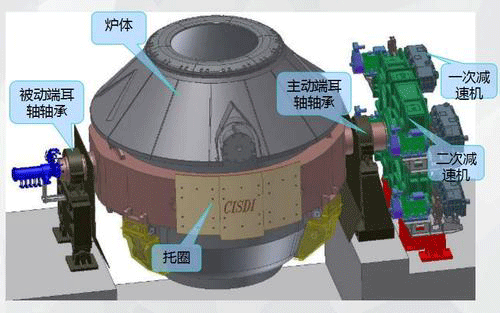
Construction and maintenance of permeable bricks for converters
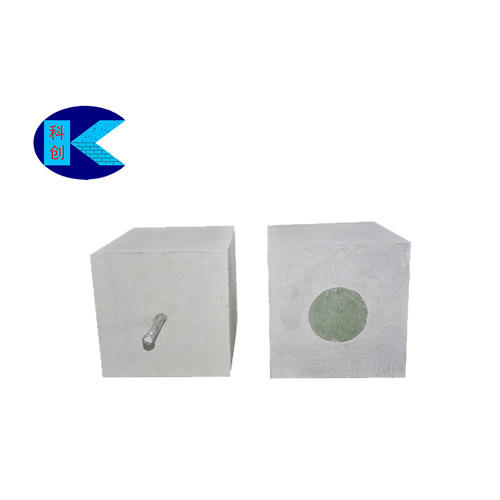
Permeable bricks are crucial equipment in the converter process. Many types exist, including split-type permeable bricks consisting of a permeable core and a base brick. Considering their development, manufacturers generally equip them with base bricks to protect the core air supply components. Other parts, such as backing bricks, may also be included. The lifespan of permeable bricks depends not only on their structural characteristics, bottom-blowing pressure, material composition, and operating processes but also on the quality of their installation.
Factors Affecting the Performance of Argon Bottom-Blown Bricks in Steel Ladles
The quality of bottom-blown argon permeable bricks in steel ladles is crucial for steelmakers. During use, adverse factors should be avoided or addressed. Factors affecting the effectiveness of bottom-blown argon permeable bricks include steel penetration of the permeable brick working surface, blockage of permeable bricks (slit type) by slag, changes in material properties, fluctuations in gas source pressure, and prolonged ladle downtime.
Several factors affecting the use of steel ladle lining
Refractory materials used for steel ladle linings include porous bricks, water-mouth bricks, magnesia-carbon bricks, castables, etc. Aside from the influence of the ladle lining materials themselves, certain factors can accelerate their consumption during use, leading to a shorter lifespan.
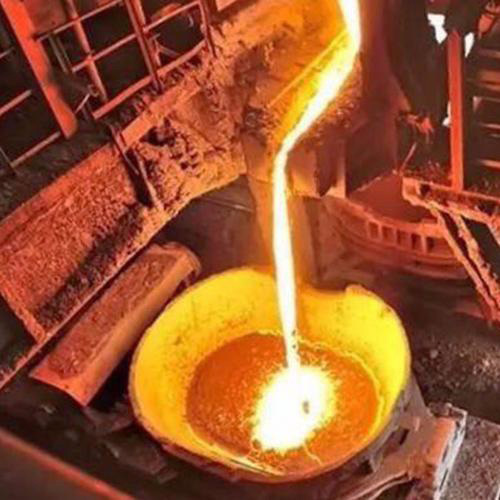
Reasons for using argon-blown porous brick ladles after refining before continuous casting
After the molten steel in the ladle is refined by continuous argon blowing through porous plugs, it will be sent to the continuous casting machine. The role of continuous casting is to continuously cast the refined molten steel to produce the final product of steelmaking: qualified steel ingots or billets.
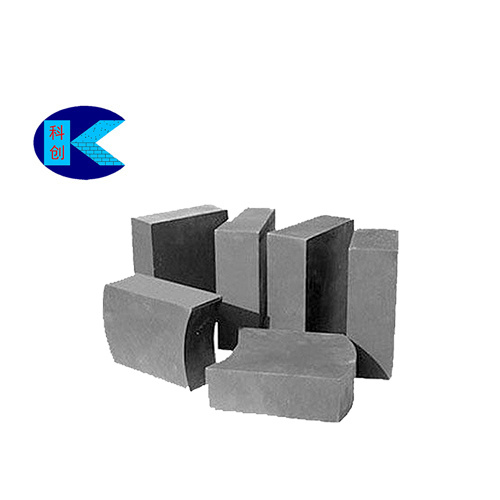
Several methods to reduce the erosion of magnesia-carbon bricks in refractory materials
In addition to permeable bricks and water-mouth bricks, magnesia-carbon bricks are essential refractory materials used in steel ladles. Magnesia-carbon bricks are composite refractory materials made from high-melting-point magnesia and high-melting-point carbon materials that are difficult to be infiltrated by slag, with various non-oxide additives added as binders. They are mainly used in steel ladle slag lines, converters, and electric arc furnaces.